[playground] Tensorflow.Js & Typescript [3]: Modeling
Tensorflow.JS provides an application programming interface similar to Tensorflow (Python API). Although it has few choices (layers, models, optimizers), it is still helpful in some applications that need online learning on client devices.
1. APIs:
Sometimes useful:
- Layers API:
tf.layers.dense,tf.layers.dropout,tf.layers.embedding,tf.layers.dense(elu, hardSigmoid, linear, relu, relu6, selu, sigmoid, softmax, softplus, softsign, tanh, swish, mish), - Model API:
tf.sequential,tf.model. - Build-In Optimizers: sgd, adagrad, adadelta, adam, adamax, rmsprop.
- Build-In Loss functions:
tf.losses.absoluteDifference,tf.losses.meanSquaredError,tf.losses.logLoss,tf.losses.huberLoss,tf.losses.hingeLoss,… (add some simple custom loss functions)
2. Example Linear Regression:
Do linear regression in the web browser (for easy visualization). The setup is the same as tutorial 1 with some extra libraries (vega, vega-embed, vega-lite):
import { Tensor, Tensor2D, tensor2d } from "@tensorflow/tfjs";
import embed from "vega-embed";
import * as tf from "@tensorflow/tfjs";
try {
// I know. I'm lazy :-D
tf.setBackend("webgl");
} catch (err) {
console.log(err);
}
document.querySelector("#device")!!.innerHTML =
`Backend by: ${tf.getBackend()}`;
function make_synthetic_data(true_w: number, true_b: number) {
let x: tf.Tensor1D = tf.randomUniform([100], 0.0, 12.0);
let noise = tf.randomNormal([100], 0, 1);
let y = x.mul(tf.scalar(true_w)).add(tf.scalar(true_b)).add(noise);
return { "x": x, "y": y };
}
let data = make_synthetic_data(2, 3);
let vegaData: { x: number; y: number }[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < data.x.size; i++) {
vegaData.push({ "x": data.x.dataSync()[i], "y": data.y.dataSync()[i] });
}
let model = tf.sequential();
model.add(tf.layers.dense({ inputShape: [1], units: 1 }));
model.compile({
optimizer: "sgd",
loss: "meanSquaredError",
});
model.summary();
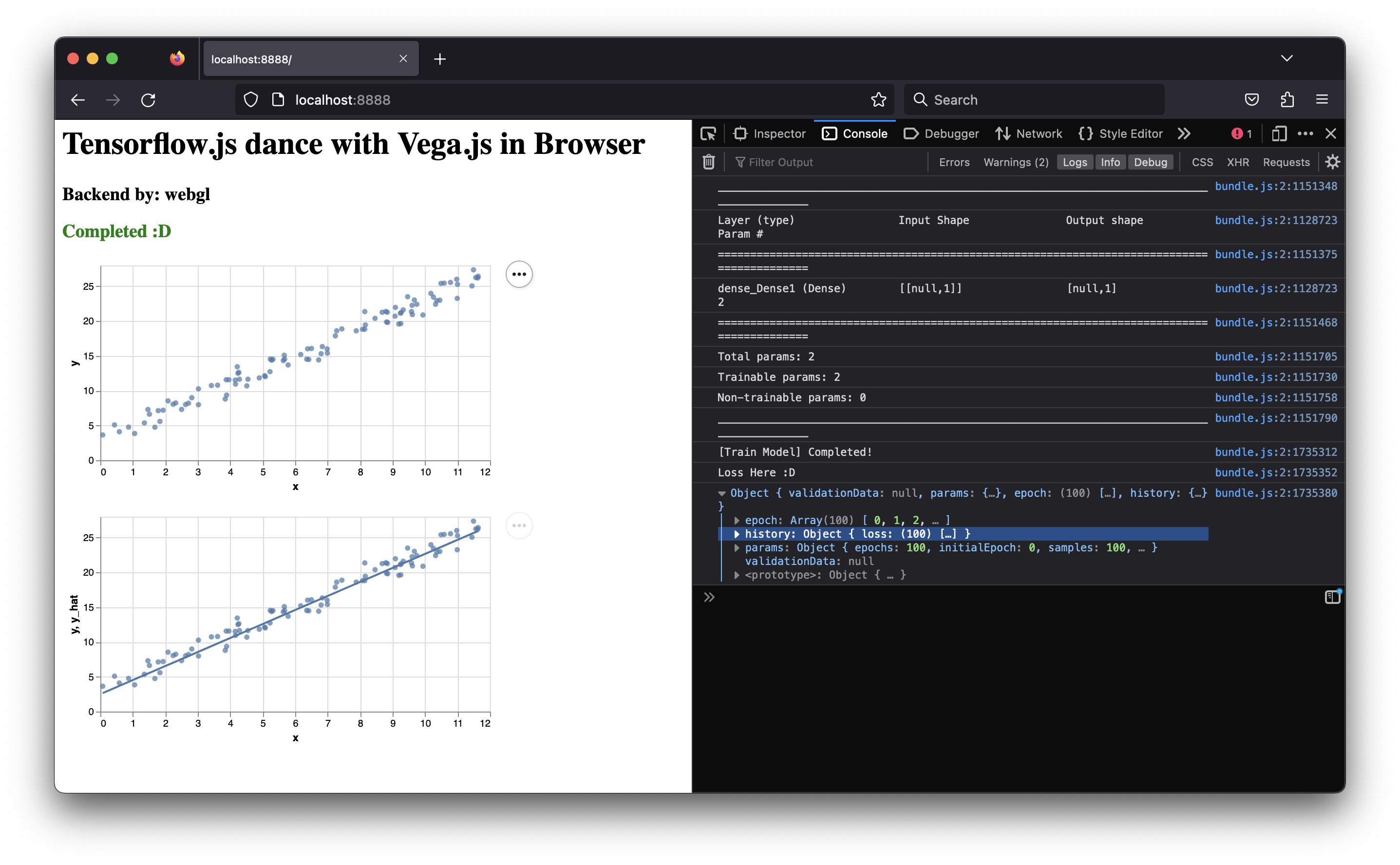
model.fit(data.x, data.y, { epochs: 100 }).then((history) => {
document.querySelector("#status")!!.innerHTML = "Completed :D";
document.querySelector("#status")!!.setAttribute("style", "color: green");
const prediction = (model.predict(data.x) as tf.Tensor)
.dataSync();
// console.log(`data sync ${prediction}`);
console.log("[Train Model] Completed!");
console.log("Loss Here :D");
console.log(history)
let finalPlotData = [];
for (let i = 0; i < data.x.size; i++) {
finalPlotData.push({
"x": data.x.dataSync()[i],
"y": data.y.dataSync()[i],
"y_hat": prediction[i],
});
}
// @ts-ignore
var speclinear = {
"$schema": "https://vega.github.io/schema/vega-lite/v5.json",
"width": 400,
"height": 200,
data: {
values: finalPlotData,
},
"layer": [{
"mark": "circle",
"encoding": {
"x": { "field": "x", "type": "quantitative" },
"y": { "field": "y", "type": "quantitative" },
},
}, {
"mark": "line",
"encoding": {
"x": { "field": "x", "type": "quantitative" },
"y": { "field": "y_hat", "type": "quantitative" },
},
}],
};
// @ts-ignore
embed("#linearregression", speclinear);
});
var specDataPoint = {
"$schema": "https://vega.github.io/schema/vega-lite/v5.json",
"width": 400,
"height": 200,
data: {
values: vegaData,
},
"mark": "circle",
"encoding": {
"x": { "field": "x", "type": "quantitative" },
"y": { "field": "y", "type": "quantitative" },
},
};
// @ts-ignore
embed("#vis", specDataPoint);
:-) and… don’t forget tf.tidy